c8.1GAS|GameplayAbility实践-翻滚、受击
大约 6 分钟
回顾
网络权限
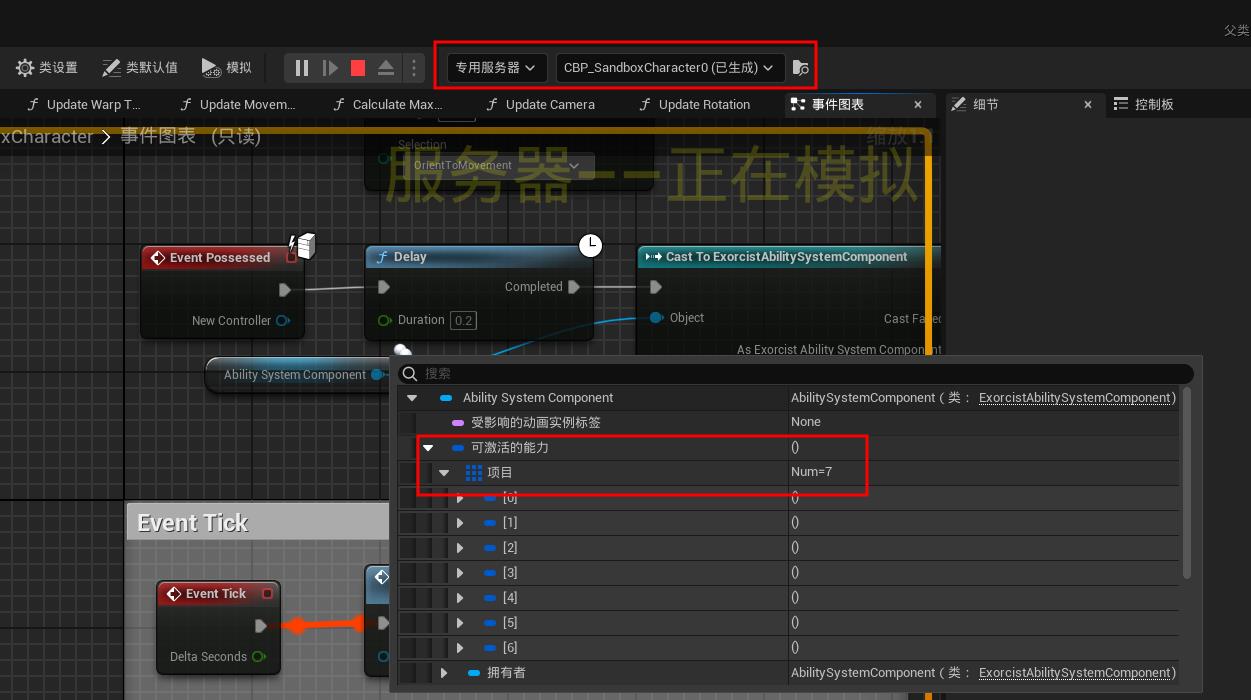
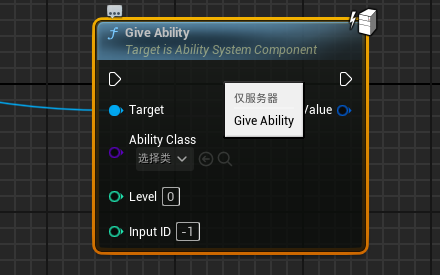
GiveAbility
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, BlueprintAuthorityOnly, Category = "Gameplay Abilities", meta = (DisplayName = "Give Ability", ScriptName = "GiveAbility"))
FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle K2_GiveAbility(TSubclassOf<UGameplayAbility> AbilityClass, int32 Level = 0, int32 InputID = -1);
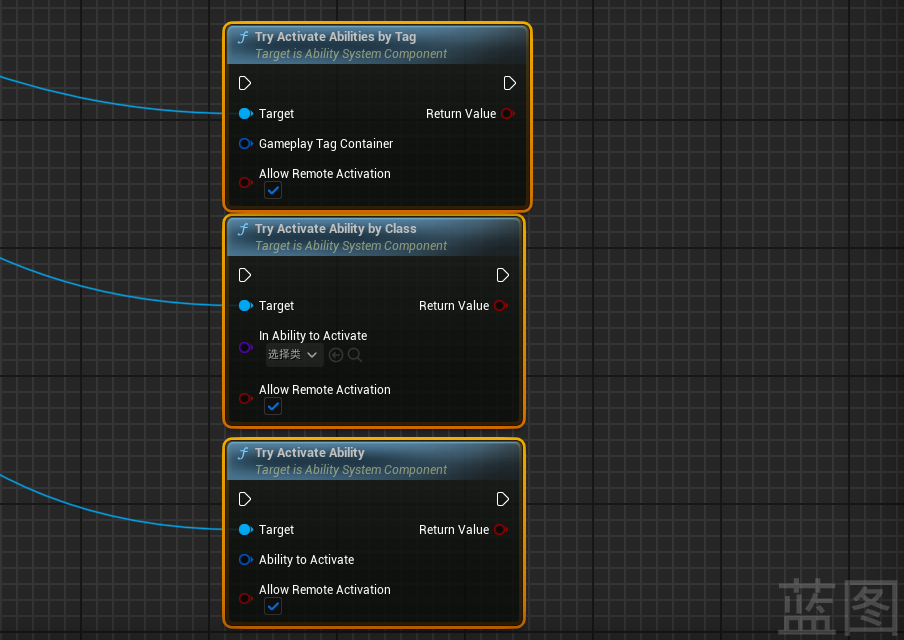
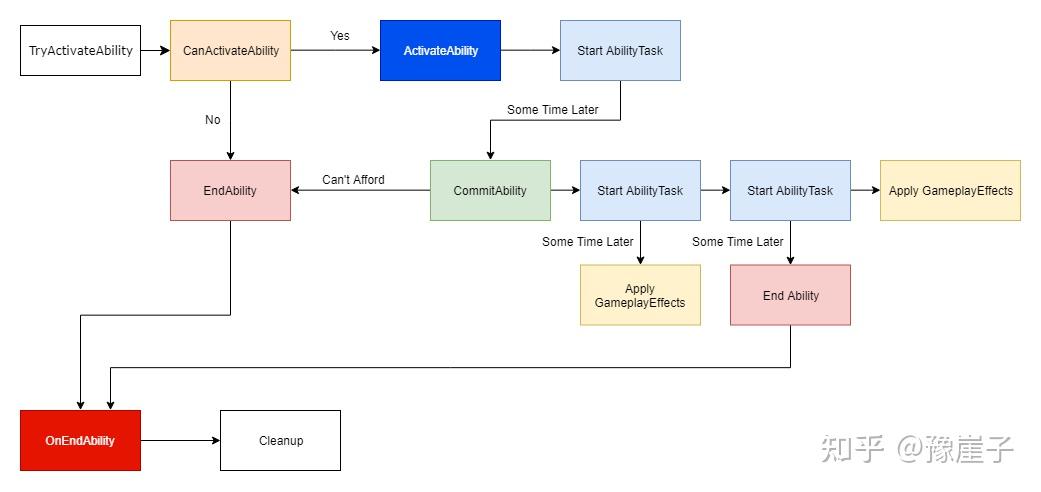
- 能力激活
- 激活请求: 玩家或游戏逻辑触发能力的激活,通常通过调用
ActivateAbility方法。 - 能力检查: 通过
CommitAbility方法检查能否激活能力(例如,检查能量、状态等)。
- 能力执行
- 任务创建: 在能力中,可以创建和启动任务(如
AbilityTask),这些任务可以处理异步操作或延时执行。 - 任务激活: 任务的
Activate方法被调用,任务开始运行。
- 结果处理
- 结束能力: 一旦完成所有操作,调用
EndAbility方法结束能力的执行,并处理可能的状态更新。
/**
* Attempts to activate the given ability, will check costs and requirements before doing so.
* Returns true if it thinks it activated, but it may return false positives due to failure later in activation.
* If bAllowRemoteActivation is true, it will remotely activate local/server abilities, if false it will only try to locally activate the ability
*/
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Abilities")
bool TryActivateAbility(FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle AbilityToActivate, bool bAllowRemoteActivation = true);
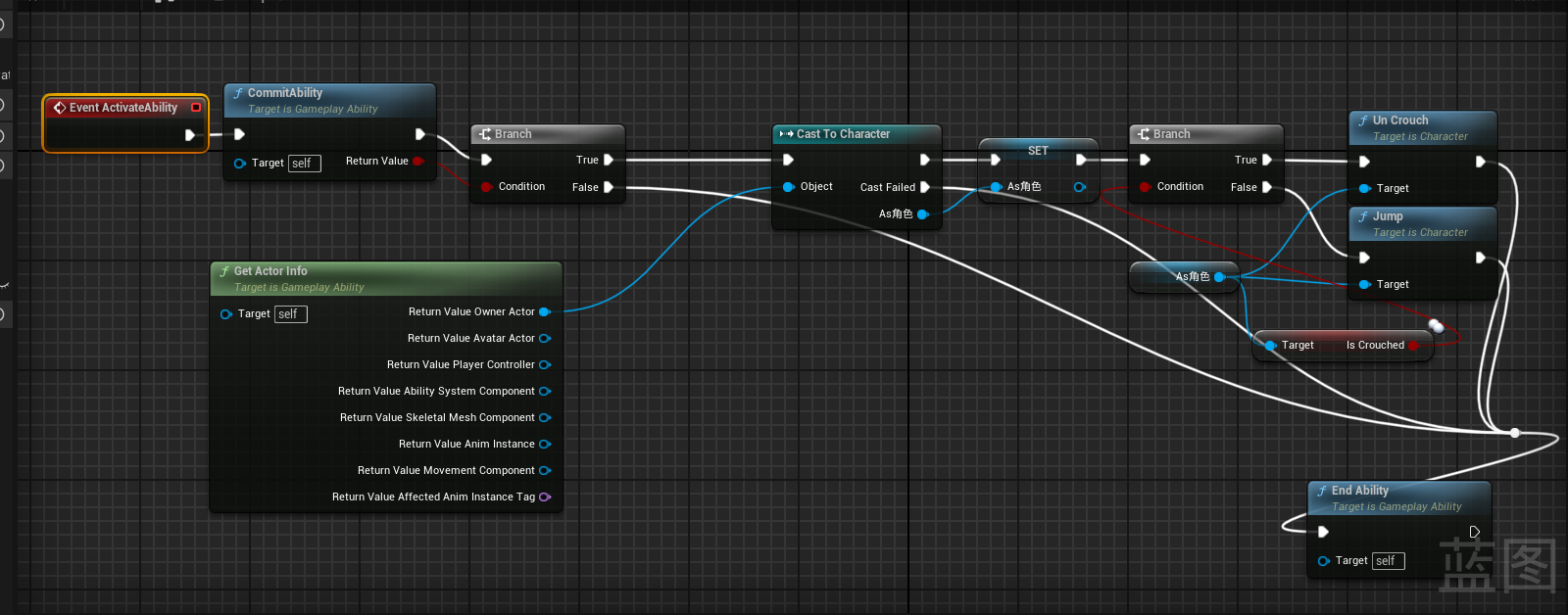
实践1|闪避
1.AbilityTask_WaitGameplayEvent
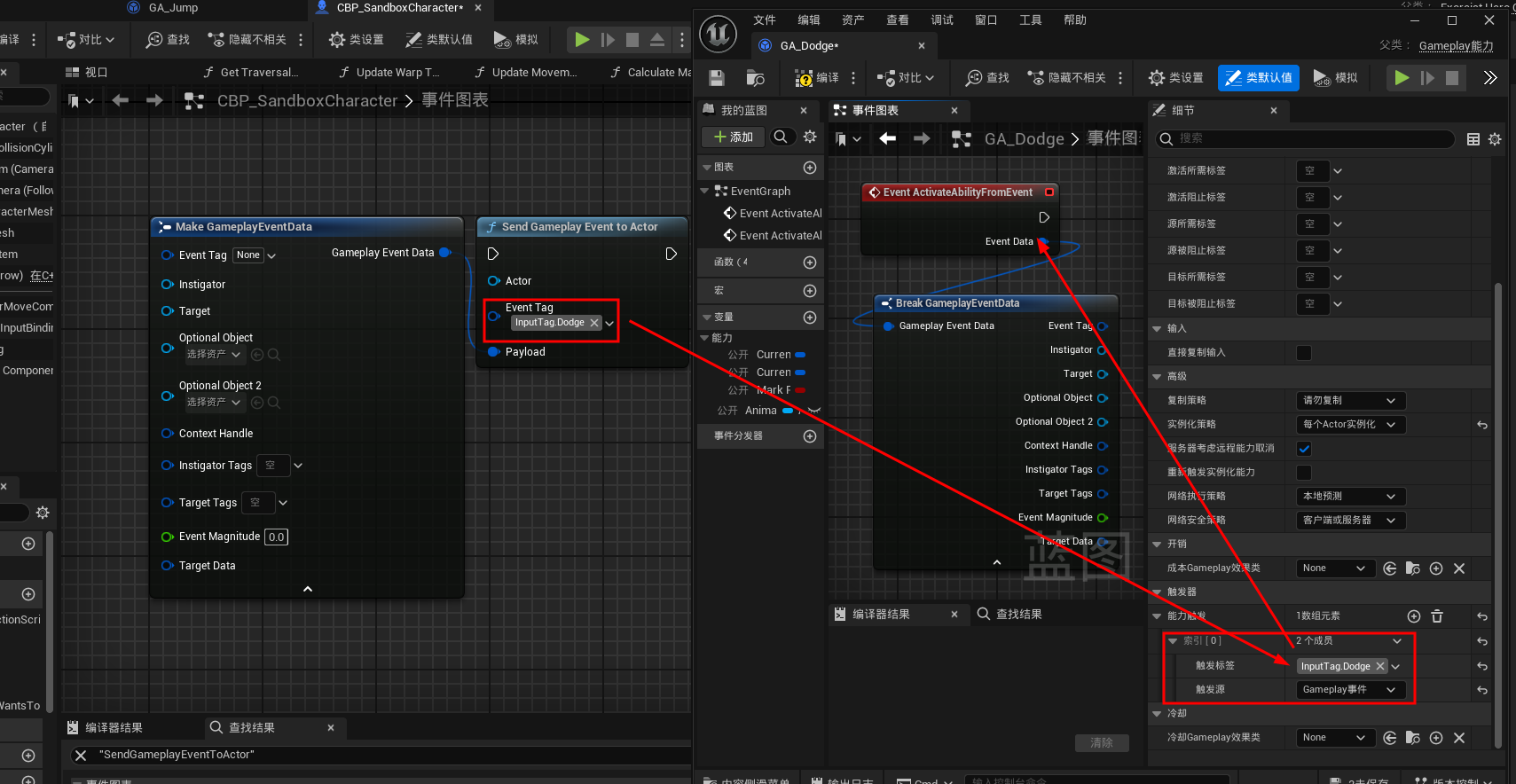
2.SendGameplayEventToActor
方向计算
EDirectionType UAbilityUtility::DeterminePlayerInputDirection(const APawn* Pawn)
{
if(!Pawn ||!Pawn->InputComponent) return EDirectionType::Invalid;
// 计算相对方向向量
const FVector InputDirection = Pawn->GetLastMovementInputVector().GetSafeNormal();
if (InputDirection.IsNearlyZero())
{
return EDirectionType::Forward; // 默认向前
}
float ForwardDot = FVector::DotProduct(InputDirection, Pawn->GetActorForwardVector());
float RightDot = FVector::DotProduct(InputDirection, Pawn->GetActorRightVector());
if (ForwardDot > 0.5f)
{
return EDirectionType::Forward;
}
if (ForwardDot < -0.5f)
{
return EDirectionType::Backward;
}
if (RightDot > 0.5f)
{
return EDirectionType::Right;
}
if (RightDot < -0.5f)
{
return EDirectionType::Left;
}
return EDirectionType::Forward;
}
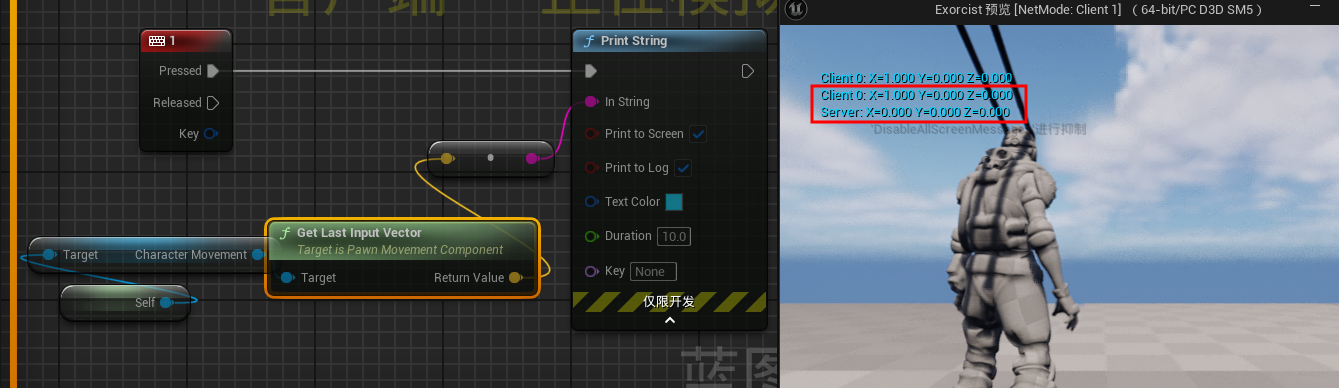
注
扩展- GetLastInputVector 和 GetLastMovementInputVector区别传送门
AbilityTasks
UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection.cpp
#include "AbilitySystem/AbilityTasks/AbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection.h"
#include "AbilitySystemComponent.h"
#include "AbilitySystem/AbilityLib/EDirectionType.h"
#include "AbilitySystem/AbilityLib/AbilityUtility.h"
UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection* UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection::CreateCalculateInputDirectionTask(UGameplayAbility* OwningAbility)
{
UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection* MyTask = NewAbilityTask<UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection>(OwningAbility);
return MyTask;
}
void UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection::Activate()
{
Super::Activate();
const bool bIsLocallyControlled = Ability->GetCurrentActorInfo()->IsLocallyControlled();
// 如果是本地控制,则发送预测请求
if (bIsLocallyControlled)
{
SendActionDirectionToServer();
}
else
{
const FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle SpecHandle = GetAbilitySpecHandle();
const FPredictionKey ActivationPredictionKey = GetActivationPredictionKey();
AbilitySystemComponent.Get()->AbilityTargetDataSetDelegate(SpecHandle, ActivationPredictionKey).AddUObject(this, &UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection::OnActionDirectionReplicated);
const bool bCalledDelegate = AbilitySystemComponent.Get()->CallReplicatedTargetDataDelegatesIfSet(SpecHandle, ActivationPredictionKey);
if (!bCalledDelegate)
{
SetWaitingOnRemotePlayerData();
}
}
}
void UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection::SendActionDirectionToServer()
{
// 使用预测窗口来封装客户端到服务器的预测机制
FScopedPredictionWindow ScopedPrediction(AbilitySystemComponent.Get());
const APawn* Character = Cast<APawn>(Ability->GetCurrentActorInfo()->AvatarActor.Get());
if (!Character)
{
EndTask(); // 如果角色无效,结束任务
return;
}
// 根据输入方向判断动作类型
const EDirectionType ActionDirection = UAbilityUtility::DeterminePlayerInputDirection(Character);
// 封装方向枚举到一个简单的数据结构中进行传输
FGameplayAbilityTargetDataHandle DataHandle;
FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum* Data = new FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum();
Data->EnumValue = ActionDirection;
DataHandle.Add(Data);
// 发送数据到服务器
AbilitySystemComponent->ServerSetReplicatedTargetData(
GetAbilitySpecHandle(),
GetActivationPredictionKey(),
DataHandle,
FGameplayTag(),
AbilitySystemComponent->ScopedPredictionKey);
if (ShouldBroadcastAbilityTaskDelegates())
{
ValidDirection.Broadcast(ActionDirection);
}
}
void UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection::OnActionDirectionReplicated(const FGameplayAbilityTargetDataHandle& DataHandle, FGameplayTag ActivationTag)
{
// 提取枚举类型的方向
AbilitySystemComponent->ConsumeClientReplicatedTargetData(GetAbilitySpecHandle(), GetActivationPredictionKey());
if (ShouldBroadcastAbilityTaskDelegates())
{
for(auto Data : DataHandle.Data)
{
if (Data)
{
GEngine->AddOnScreenDebugMessage(-1, 5.0f, FColor::Red, TEXT("OnActionDirectionReplicated"));
FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum* HitResultPtr = static_cast <FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum*>(Data.Get());
if (HitResultPtr)
{
ValidDirection.Broadcast(HitResultPtr->EnumValue);
}
}
}
}
}
AbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection.h
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "Abilities/Tasks/AbilityTask.h"
#include "AbilitySystem/AbilityLib/AbilityUtility.h"
#include "AbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection.generated.h"
// 自定义结构用于传递简单的枚举值
USTRUCT(BlueprintType)
struct FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum : public FGameplayAbilityTargetData
{
GENERATED_USTRUCT_BODY()
// 用于存储简单的枚举值 (例如方向类型)
UPROPERTY(BlueprintReadWrite, EditAnywhere, Category = Targeting)
EDirectionType EnumValue;
virtual UScriptStruct* GetScriptStruct() const override { return FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum::StaticStruct(); }
virtual FString ToString() const override { return FString::Printf(TEXT("EnumValue: %d"), static_cast<uint8>(EnumValue)); }
bool NetSerialize(FArchive& Ar, UPackageMap* Map, bool& bOutSuccess)
{
//Ar << EnumValue; // 序列化 EnumValue
Ar.SerializeBits(&EnumValue, 3);
bOutSuccess = true;
return true;
}
};
// 使结构可以通过网络序列化
template<>
struct TStructOpsTypeTraits<FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum> : public TStructOpsTypeTraitsBase2<FGameplayAbilityTargetData_SimpleEnum>
{
enum
{
WithNetSerializer = true,
};
};
UCLASS()
class EXORCIST_API UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection : public UAbilityTask
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
DECLARE_DYNAMIC_MULTICAST_DELEGATE_OneParam(FInputDirectionDelegate, EDirectionType, DirectionType);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category="Ability|Tasks", meta = (DisplayName = "CreateGetInputDirectionTask", HidePin = "OwningAbility", DefaultToSelf = "OwningAbility", BlueprintInternalUseOnly = "true"))
static UAbilityTask_CalculateInputDirection* CreateCalculateInputDirectionTask(UGameplayAbility* OwningAbility);
UPROPERTY(BlueprintAssignable)
FInputDirectionDelegate ValidDirection;
private:
virtual void Activate() override;
UFUNCTION()
void SendActionDirectionToServer();
UFUNCTION()
void OnActionDirectionReplicated(const FGameplayAbilityTargetDataHandle& DataHandle, FGameplayTag ActivationTag);
};
实例化策略
| 实例化类型 | 描述 | 优点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 按执行实例化 | 每次技能运行时生成新对象副本。 | 可自由使用蓝图和成员变量,所有内容在执行前初始化。 | 不频繁运行的技能,例如MOBA中的"终极技能"。 |
| 按Actor实例化 | 每个Actor在首次执行时生成技能实例,以后复用。 | 减少新对象创建的开销,适合大规模使用技能。 | 大型战斗中频繁使用的技能,例如小兵的基本攻击。 |
| 非实例化 | 使用类默认对象,不生成任何新实例。 | 效率最高,无需创建对象,节省资源。 | 高频率执行且不需内部变量的技能,例如RTS中的基本攻击。 |
.png)
